

Working fluids can be air, hot water, pressurized water or even liquid sodium, heated in some kind of boiler.Ī large number of different designs for ICEs have been developed and built, with a variety Not consisting of, mixed with, or contaminated by combustion products. The internal combustion engine (or ICE) is quiteĭifferent from external combustion engines, such as steam or Stirling engines, in which the energy is delivered to a working fluid
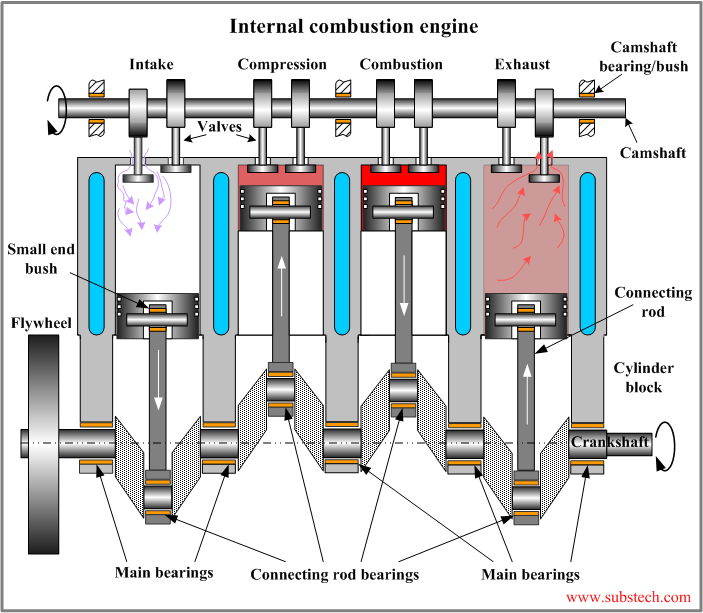
A second class of internal combustion engines useĬontinuous combustion: gas turbines, jet engines and most rocket engines, each of which are internal combustion engines on
Is intermittent, such as the more familiar four-stroke and two-stroke piston engines, along with variants, such as the six-stroke piston engine and the Wankel rotary engine. The term internal combustion engine usually refers to an engine in which combustion This force moves the component over a distance, Of the high-temperature and -pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine, such as pistons, turbine blades, or a nozzle. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion This innovative engine could save fuel up to 10%–18% in all frequently-used working conditions of a general vehicle IC engine.The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel (normally a fossil fuel) occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber. According to the simulation results, compared with the original engine, the fuel saving rate map of the 2/4-stroke switchable secondary expansion IC engine was made by combining the high fuel saving rate conditions of the 2-stroke and 4-stroke working modes. The experiment results showed that the fuel consumption of the engine working on the 4-stroke secondary expansion mode was lower than that of the original engine. A GT-Power simulation model was established as the supplement of the experiment to evaluate the 2/4-stroke switchable secondary expansion IC engine. A traditional 4-cylinder gasoline IC engine was transformed into a secondary expansion IC engine, however, without the valve time switching device, its expansion cylinder could only work on the 4-stroke working mode. The 2-stroke secondary expansion mode has great advantages in high load condition on both fuel efficiency and power output, but it is not suitable in low load condition, so the 4-stroke secondary expansion is applied to maintain the high energy conversion efficiency in the low load condition. The expansion cylinder could switch its working mode between 2-stroke and 4-stroke to perform different secondary expansion modes just by varying the valve timing. The 2/4-stroke switchable secondary expansion IC engine is a 4-cylinder engine with two combustion cylinders and two expansion cylinders. The secondary expansion means the burned gas, after working in a traditional 4-stroke combustion cylinder, is transferred into another cylinder to expand again.

To develop an internal combustion (IC) engine with high energy conversion efficiency, simple structure, and high reliability, a 2/4-stroke switchable secondary expansion IC engine concept is proposed in this paper.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
